By Reece Hayden | 2Q 2023 | IN-6920
Registered users can unlock up to five pieces of premium content each month.
Hyperscalers Target Startup Incubation as a Path toward Enterprise Generative AI Commercialization |
NEWS |
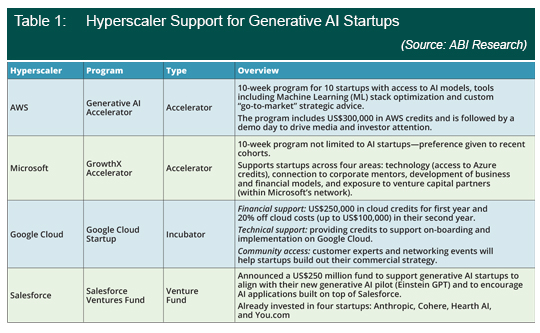
With Bard, GPT-3, Einstein GPT, and Ernie Bot, and now Alibaba getting into the game, hyperscalers are evidently at the forefront of generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology. However, the path from technology development to monetization remains murky. Hyperscalers are turning to startups as a potential route toward generative AI monetization. Currently, they are pursuing three types of strategic initiatives to support startup development: 1) incubation (help build ideas into a product and then scale out a business model and company, little or most likely no equity taken in company); 2) acceleration (the company is required to have a minimum viable product and be looking for seed-stage funding, little or most likely no equity taken in company); and 3) venture funding (investment in early-stage startups with a significant portion of equity taken by investor). Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Salesforce are the latest players to announce initiatives aimed at tapping into the potential commercial value offered by generative AI startups. Table 1 provides a breakdown of each startup support initiative.
How Will Startups Help Hyperscaler-Led Generative AI Commercialization? |
IMPACT |
- Support Their Traditional Usage-Based Business Model: The traditional hyperscaler revenue model is based on the volume of resources used by customers. Enabling startups to build applications on top of their resources will encourage enterprise usage and drive existing revenue streams. Propping up existing hyperscaler revenue streams is vital given the slowdown in public cloud growth.
- Efficiently Build Generative AI Marketplace: Partnering with startups will begin to create an AI application marketplace. These app stores will not only help drive resource usage, but also allow hyperscalers to drive new revenue streams through application-based “revenue sharing” agreements. Although hyperscalers can, and will, build apps in-house, given the time, cost, and vertical-expertise inhibitors, leveraging partnerships with startups to build collaborative applications will be most resource efficient.
- Move from Incubation to Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) or Investment: Accelerators and incubators should be viewed as a test bed for potential hyperscaler investment or M&A opportunities. These programs can help hyperscalers grow their capital reserves by tapping into the applications with the best product and market opportunity. This will be important given the renewed emphasis on big-tech venture capital.
- Market Expertise and Innovative Ideas: Given the immaturity of the technology, investment/innovation remains top of mind for hyperscalers. Startup incubators/accelerators will enable hyperscalers to understand the enterprise vertical market more effectively to align their investment roadmap and resource allocation to meet emerging pressure points and expectations.
Hyperscalers Are Not Alone, Startup Incubation Will Create Value for Other Stakeholders |
RECOMMENDATIONS |
Given hyperscaler activity, should other players looking to position themselves as generative AI leaders build startup support programs? The answer is yes. But who do we think would be suited? Two key groups stand out: hardware vendors (e.g., Intel) and System Integrators (SIs) (e.g., Tata Consultancy Services). These core stakeholders could leverage startups to favorably position themselves within the increasingly competitive generative AI market as follows:
- Hardware Vendors: Hardware is a crucial component of AI, but as this market matures, vendors will want to transition toward the software side to access its huge revenue opportunity. Startups can provide vendors with software expertise and experience, while also helping guide hardware strategic investment through alignment with enterprise expectations and applications. NVIDIA’s Inception from Startups (which provides technology, expertise, co-marketing, and access to investors) has already targeted the generative AI opportunity by supporting VinBrain (a detection application for healthcare).
- System Integrators: As generative AI applications/services are deployed, SIs will help vendor package solutions most effectively solve enterprise pain points and then bring them to market to support vendor commercialization. This role means working between application developers (startups) and hyperscalers; subsequently, SIs should look to build a strong ecosystem of AI startup partners, as it will help position themselves as leaders in this emerging market, while also helping to define their long-run commercial strategy.
Generative AI remains in an early stage both technologically and commercially. Market incumbents (hyperscalers/hardware vendors) and prospective stakeholders (SIs) must already start to build out their position. Developing ties to startups through investment or incubation will help build each stakeholder’s market brand and contribute toward constructing long-term commercial opportunities.