Finding Solutions to Current and Future 5G-as-a-Service (5GaaS) Challenges
Log In to unlock this content.
You have x unlocks remaining.
This content falls outside of your subscription, but you may view up to five pieces of premium content outside of your subscription each month
You have x unlocks remaining.
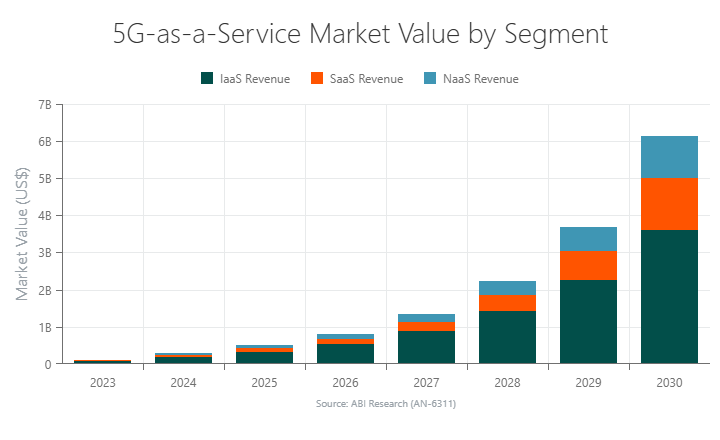
Market Overview
5G-as-a-Service (5GaaS) is still in its early stages, particularly when compared to traditional Capital Expenditure (CAPEX)-heavy private 5G network deployments. However, with increasing interest in as-a-Service (aaS) offerings, ABI Research forecasts that the market will reach US$6.1 billion by 2030, growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 76%.
By segment, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) will grow at 74%, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) at 83%, and Network-as-a-Service (NaaS) will see a 72% increase. SaaS (telco-specific software) will experience the fastest growth due to its scalability, virtual nature, and the outsourcing of complex tasks like network setup and maintenance. Despite this, IaaS revenue remains dominant, given the high cost of hardware implementations for 5G connectivity on a subscription model.
The expansion of 5GaaS will also be fueled by the limitations of incumbent Wi-Fi technologies, which fall short in supporting next-gen enterprise applications. For example, Wi-Fi is insufficient for Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs), where low-latency handovers are critical. 5G is already complementing Wi-Fi in some applications, and this unification will only increase in occurrence.
Affordable, flexible, and compact 5GaaS solutions, particularly those using leased hardware models, will drive broader adoption in the private sector. These solutions provide businesses with the opportunity to test 5G technology's impact on operational efficiency without committing to permanent infrastructure investments.
“Much of 5GaaS adoption revolves around a need for connectivity, as well as embodying a supplementary overlay to Wi-Fi, especially in mobility-oriented implementations. However, as a supporting device ecosystem has only recently emerged, specific use case adoption remains slow. Regardless, several firms have started to build solutions around this, which will aid in speeding up market diffusion.” – Shadine Taufik, Analyst at ABI Research
Current 5GaaS Challenges and Solutions
Economic Downturn
With many businesses cutting costs during the economic slowdown, adopting 5GaaS may not be a top priority unless a clear Return on Investment (ROI) is evident. For example, around 45% of manufacturing firms are still in the planning phase for 5G implementation, largely due to the need for significant cost savings and operational efficiency.
Solution: Efficient Resource Utilization
In the face of an economic downturn, 5GaaS can offer a more cost-effective connectivity model, especially with consumption-based pricing. Vendors can emphasize these potential savings to encourage adoption, making 5GaaS a more attractive option during financially uncertain times.
Talent Shortage
A lack of qualified personnel capable of bridging the gap between telco services and enterprise needs is hindering the adoption of 5GaaS. As businesses explore new models and innovative propositions, the shortage of cross-domain experts slows the pace of 5G adoption.
Solution: Upskilling & Outsourcing
The talent shortage issue can be addressed by outsourcing consulting functions through revenue-sharing partnerships or investing in the upskilling of existing employees. This creates a more sustainable way for companies to bridge the skills gap without solely relying on external expertise.
Vendor Lock-ins
Many existing solutions are locked into proprietary systems, creating dependency on specific vendors. While bundling services can help secure early adoption, this can ultimately limit flexibility and hinder the ability to switch to different providers or integrate with other systems.
Solution: Ecosystem Building
Building interoperability between networking systems, compatible devices, and legacy infrastructure is key to successful 5G adoption. Partnerships with other industry players will help facilitate smooth transitions and reduce the risk of lock-ins, thus paving the way for greater flexibility in the 5G landscape.
Market Education
Many enterprises outside the telecoms sector don’t fully understand the value of 5G adoption. As many businesses have relied on Wi-Fi networks for years, the shift to 5G requires a greater awareness of its capabilities. Educating the market on the benefits of 5GaaS is critical to wider acceptance.
Solution: Proof of Concept & Trials
Vendors should offer Proof of Concept (PoC) or trial periods to help market education efforts. These trials allow businesses to experience tangible benefits firsthand, which can simplify the decision-making process and offer a clearer picture of 5GaaS’ real-world advantages.
Immature Device Ecosystem
The lack of compatible devices is another significant barrier. Many businesses believe that insufficient industrial devices hinder the scaling of 5G private cellular networks. Without the proper hardware to execute necessary tasks, it is challenging for companies to justify the transition to 5G. Nearly one-quarter of respondents from a recent ABI Research survey indicated that private cellular network scalability is hindered by insufficient industrial devices.
Solution: Innovation & Niche-Building
Vendors should focus on niche solutions for specific use cases that can show clear benefits of 5G adoption. Packaging these tailored solutions will help firms realize the potential of 5GaaS in a way that feels more customized and relevant to their specific needs.
Upcoming 5GaaS Challenges and Solutions
Shifting Risks
As vendors transition to 5GaaS models, they take on significant financial risks that were previously borne by customers. This shift requires firms to manage ongoing maintenance and upgrade costs, while also providing solutions at a lower fee compared to traditional product sales.
Solution: Liability Mitigation
To avoid serious financial risks, vendors should incorporate liability clauses into their 5GaaS contracts. This ensures that both parties are protected from unforeseen damages. Offering minimum commitment periods and requiring upfront payment for expensive infrastructure components, like hardware, can help mitigate potential losses.
Volatile Revenue
Economic uncertainty can cause customers to unsubscribe from non-core services, which leads to unpredictable revenue streams. During economic downturns, firms may face reduced demand for services, while in prosperous times, there may be higher expectations for performance and service availability.
Solution: Tiers & Commitments
Implementing tiered pricing systems can reduce the impact of fluctuating usage patterns by providing customers with predefined usage commitments. These multi-year commitments help vendors secure consistent revenue streams and reduce the uncertainty caused by volatile demand. Vendors can offer clear pricing models for customers to ensure stable, predictable costs.
Scalability Concerns
The ability to scale quickly during peak periods is critical for 5GaaS vendors. However, over-investment in resources during slower periods can absorb much-needed capital, while failure to meet demand during high periods can lead to dissatisfaction. Vendors need to strike the right balance to ensure service continuity without compromising financial stability.
Solution: Modularity & Caps
To address scalability challenges, vendors should offer modular solutions that cater to different business sizes, particularly for smaller companies with limited resources. Additionally, introducing consumption-based models with usage caps can help ensure that businesses only pay for what they need.
Vendors can also invest in Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based forecasting tools that can help vendors predict and meet demand more effectively, allowing for better resource allocation.
Key Companies
Conclusion
ABI Research’s 5GaaS: Business Models, Challenges, and Opportunities report provides a deep understanding of the key market dynamics, companies, and trends that are shaping the future of telecom. Download today!
Related Research

Report | 4Q 2024 | AN-6311
Related Service
- Competitive & Market Intelligence
- Executive & C-Suite
- Marketing
- Product Strategy
- Startup Leader & Founder
- Users & Implementers
Job Role
- Telco & Communications
- Hyperscalers
- Industrial & Manufacturing
- Semiconductor
- Supply Chain
- Industry & Trade Organizations
Industry
Services
Spotlights
5G, Cloud & Networks
- 5G Devices, Smartphones & Wearables
- 5G, 6G & Open RAN
- Cellular Standards & Intellectual Property Rights
- Cloud
- Enterprise Connectivity
- Space Technologies & Innovation
- Telco AI
AI & Robotics
Automotive
Bluetooth, Wi-Fi & Short Range Wireless
Cyber & Digital Security
- Citizen Digital Identity
- Digital Payment Technologies
- eSIM & SIM Solutions
- Quantum Safe Technologies
- Trusted Device Solutions


