Five Ways the Private Cellular Network Security Market Is Evolving
Here are five ways that private network security is evolving and how cybersecurity vendors should approach these shifts. Identify current challenges like endpoint security, understand the shift to new deployment models, analyze regional differences, and more.
Log In to unlock this content.
You have x unlocks remaining.
This content falls outside of your subscription, but you may view up to five pieces of premium content outside of your subscription each month
You have x unlocks remaining.
According to ABI Research, the private cellular network security market is projected to reach a US$16.2 billion sizing by 2029, a more than four-fold increase compared to 2024. But to seize this booming market, network security vendors must understand how their potential customers view telco cybersecurity.
Private cellular network security is inherently different from public networks. They have different priorities, desired use cases, and network features. The potential financial loss and damage to brand reputation from a cyberattack serve as strong motivators for enterprises to invest in private 5G security. This is especially true for data-rich industrial environments that are prime targets for attackers.
ABI Research continues to study the evolution of private network security with both qualitative and quantitative analyses. Our Securing Private Cellular Networks: Technology & Market Trends research report identifies the current challenges, customer preferences, and opportunities in the market. To help network security vendors align product portfolios with customer demand, this resource shares five ways the private network security space is evolving.
1. The Shift to as-a-Service Deployment Models
Private networks often borrow concepts from public networks. The “as-a-Service” deployment model concept is taking hold in the market. As of 2024, 36% of private network security spending was allocated to as-a-Service solutions. ABI Research forecasts that this figure will increase to 44% of total revenue as enterprise 5G customers gravitate toward software-based security tools.
ABI Research Analyst Georgia Cooke emphasizes the future-proofness of as-a-Service models. “Moving forward, all cellular networks will transition to a compute-centric model, with an increase in analytics and network automation.” She continues, “In the private network space, this drives the visibility required to move past simple network security and to improve endpoint management—which, at the moment, is lacking.”
Our analyst team anticipates strong growth for managed services in particular. Telcos and private network customers struggle to find professionals with expertise in both 5G and cybersecurity, making managed security offerings the only option for many.
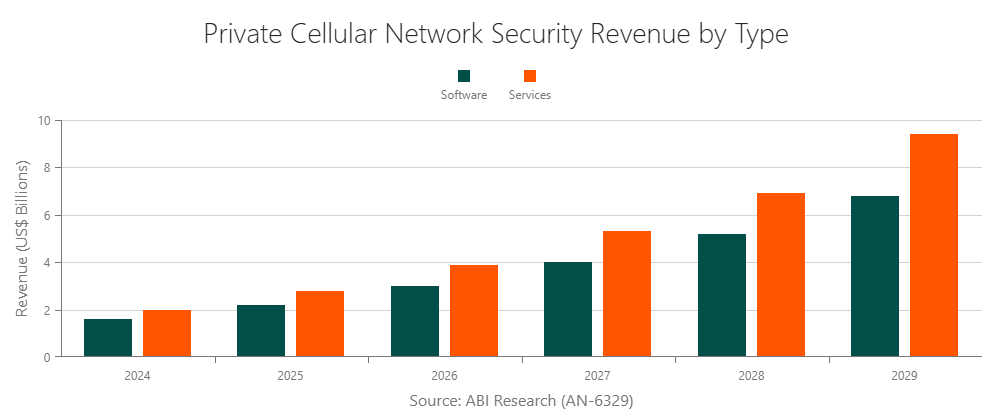
2. End-to-End Solutions Are Preferable
The typical private network customer prefers an end-to-end solution that includes connectivity, security, and device management in a single package. This greatly simplifies the deployment process and provides a better user experience.
The problem for security vendors is that Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) remain the de facto distribution partner for network customers in some regions. And most of them offer their own bundled solutions, making it unlikely they will collaborate for added functionalities.
ABI Research recommends that network security vendors work with System Integrators (SIs) to combine connectivity, operational requirements, and cybersecurity tools. Partnering with an SI will broaden brand reach and build stronger marketing momentum for these “one-stop” solutions.
3. Regional Differences Call for Market Segmentation
Cooke cautions security providers that there are regional disparities to be aware of. “The private network market is itself highly regional, with around half of all global private networks deployed in China.” She continues, “Cellular security vendors that traditionally operate outside of private network hotspots such as Asia-Pacific and the Middle East & Africa may have to overcome variance in regulatory requirements, infrastructure practices, and supply trends.”
Network security vendors from the West must address the fact that much of the market opportunity resides in Asia-Pacific and the Middle East & Africa. In addition to the differences listed above, they also must translate product documentation and offer native-language customer support. Combined, this makes catering to private networks very complex.
Given these circumstances, network security vendors must break the market into smaller segments. This way, they can tailor 5G security solutions to the specific requirements of each high-growth region in a phased approach.
4. Threat Intelligence Must Keep up With Attackers’ New Methods
Threat actors continue to evolve their tactics, making it essential for enterprises to keep pace by adopting forward-looking security solutions. Traditional threat intelligence alone will not be enough to effectively protect data-rich environments.
Industrial networks are especially prone to sophisticated cyberattacks due to their criticality and ransom potential. The transition to 5G Standalone (SA) deployments is fully underway, offering immense opportunity for developing secure-by-design greenfield sites. Security vendors can tailor tools for large-volume, low-latency traffic to appeal to industrial 5G SA customers.
Network security providers must pay particular attention to manufacturing, utilities, oil & gas, mining, and other popular targets for threat actors. This has not proven easy in the past, as educating the networking industry has been a key roadblock to wider adoption of security tools. It’s imperative for security providers to highlight the potentially disastrous effects of an attack on endpoint devices or other network entry points.
5. Private Network Security and Operational Requirements Are Well Aligned
Network automation and data analytics are key use cases for private cellular operators. While network security and operational needs often butt heads, the visibility, scalability, and orchestration required for network autonomy and analytics ensure a happy marriage with evolving security solutions.
Network security companies offer tools that naturally improve operational visibility and provide flexibility in management. This rare alignment cannot go untapped. As Cooke states, “Dedicated security vendors should emphasize the ‘double-duty’ ROI in this field, working in partnership with network automation accelerators and finding effective distribution channels to lower the barrier to entry.”
Learn more about how the private cellular network security market is evolving, who the key market players are, and how security providers should respond by reading the ABI Research report, Securing Private Cellular Networks: Technology & Market Trends.
Related Research

Report | 2Q 2025 | AN-6329
Related Service
- Competitive & Market Intelligence
- Executive & C-Suite
- Marketing
- Product Strategy
- Startup Leader & Founder
- Users & Implementers
Job Role
- Telco & Communications
- Hyperscalers
- Industrial & Manufacturing
- Semiconductor
- Supply Chain
- Industry & Trade Organizations
Industry
Services
Spotlights
5G, Cloud & Networks
- 5G Devices, Smartphones & Wearables
- 5G, 6G & Open RAN
- Cellular Standards & Intellectual Property Rights
- Cloud
- Enterprise Connectivity
- Space Technologies & Innovation
- Telco AI
AI & Robotics
Automotive
Bluetooth, Wi-Fi & Short Range Wireless
Cyber & Digital Security
- Citizen Digital Identity
- Digital Payment Technologies
- eSIM & SIM Solutions
- Quantum Safe Technologies
- Trusted Device Solutions
