3Q 2020 | IN-5886
Registered users can unlock up to five pieces of premium content each month.
Fitness Applications Can Strengthen AR/VR Device Value Proposition for Consumers |
NEWS |
The introduction of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) applications in fitness and personal training is a growing area that promises to expand sport and gym experiences while empowering individuals to better achieve their fitness goals and improve their performance and health with novel tools.
VR Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs) and fitness applications are increasingly mature, providing consumers a range of options from video games that integrate exercise to VR yoga classes by the sea and VR boxing courses with the assistance of avatars. Users have the chance to exercise in VR in the comfort of their homes, which has proven very effective in helping individuals remain fit and active during the COVID-19 pandemic. At the same time, online fitness and fitness apps noticed a major boom even before the lockdowns, which can also drive the demand for VR exercise further. The first wave of virtual gyms, such as Black Box and VR Fit, are already a reality, providing the opportunity to incorporate VR into your fitness routine at an affordable price while more and more real world gyms are providing VR headsets to enhance certain types of exercises, such as cycling. Regarding the introduction of AR in fitness, consumer smart glasses can be a key enabler for data visualization during ar fitness and sports games, such as Oculus basketball training game Big Ballers. But just as importantly, AR and VR fitness ensures user safety thanks to pass-through display technology. ABI Research forecasts that AR smart glasses shipments for sports and fitness will reach approximately 2.2 million units in 2027, while AR guidance and instructions will lead among AR fitness use cases.
Chart 1: Sports and Fitness Smart Glasses Shipments of Monocular Form Factor World Markets (Source: ABI Research)
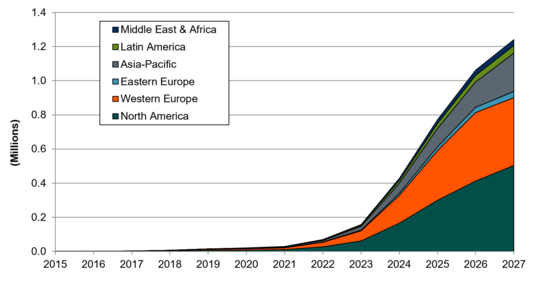 |
|
Chart 2: Sports and Fitness Smart Glasses Shipments of Binocular Form Factor World Markets (Source: ABI Research)
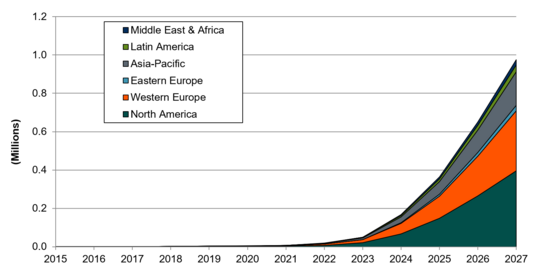 |
The experience from the market so far has proven that the combination of exercise and gaming (such as Nintendo Wii Fit, Microsoft Kinect, or Pokémon Go) and the capability to intuitively access and understand healthcare/fitness data (smartwatches) increases motivation for exercise and demand for solutions that enhance/differentiate traditional training experiences. At the same time, the demand for home exercise/on-demand content and the value of feedback and guidance from professionals will contribute to the usage of AR and VR headsets as a fitness tool going forward, unlocking new opportunities for use cases that provide tangible value to smart glasses users and new opportunities to target wider audiences.
How VR and AR Can Empower Training |
IMPACT |
The concept of virtual gyms/sports was designed in order to reshape and enhance gym routines and traditional indoor cycling and motivate users to introduce exercise to their daily routines and maintain it as a long-term lifestyle. For instance, the introduction of interactive gaming experiences in combination with exercise goals has the ability to distract users from focusing on muscle pain and encourage effort. The concept of pain distraction is similar with VR wellness therapy applications. In addition, VR applications such as HOLOFIT VR Fitness allow users to escape from monotonous stationary bikes and ellipticals by immersing them in virtual trips and landscapes. At the same time, VR fitness apps allow users to monitor performance and tailor exercise programs in accordance with their personal needs and goals. However, VR fitness apps are still a supplemental exercise option, primarily due to VR HMD limitations such as device weight, battery life, motion sickness, and heat release. In addition, VR exercise is not suitable for all types of physical activity (such as weightlifting) due to its full immersion in a virtual world. In order to speed heart rate and combine weight-based training elements, VR providers include some accessories that are safe to use in VR.
The introduction of AR and Mixed Reality (MR) smart glasses in fitness and personal training allow individuals to exercise smarter by creating personalized experiences and overlaying performance metrics and data, such as distance coverage, time, calories, heart rate, etc., in their field of view. MR consumer devices also have the potential to bring virtual personal trainers to life; Samsung has demonstrated a personal training session with the assistance of a virtual trainer and the company’s potential AR headset. The establishment of AR in fitness is still a niche area, but some AR smart glass manufacturers have already developed devices only suitable for sports, Some of those companies include the following:
- Solos’ smart glasses, designed for cycling
- Vuzix Labs’ Smart Swim
- FORM’s Smart Swim Goggles
There is also the mobile device AR market, which foregoes head-worn opportunities but can still leverage the growth of online fitness applications and assist users with services like virtual trainers that show step-by-step instructions.
Are AR Smart Glasses the Future Fitness Tracking Wearables? |
RECOMMENDATIONS |
The demand for wearable technology and, more specifically, fitness tracking smartwatches, has dramatically risen the last couple of years. Not only is this because the market offers a wide range of smartwatch options in various designs, styles, and prices, but also because of changes in consumer behavior. Consumers have generally accepted a more health-conscious and proactive mindset when it comes to technology. Smartwatches have significantly advanced over the past few years and can be used in a range of different types of exercise, from swimming to dancing and aerobics, while still providing accurate and rich data about a user’s performance and health status. In addition, the convenient and immediate access to simple physical activity/healthcare data not only assists in self-healthcare monitoring but also contributes to boosting users’ motivation for exercise.
Consumer AR smart glasses are a promising upcoming wearable type that has huge potential to become an important player in fitness tracking and eventually reshape market trends in the fitness space long term. Hands-free access to exercise/activity data in a user’s field of view is a main competitive advantage of smart glasses over smartwatches, which is important for sports such as cycling or skiing where users cannot check their wrists. At the same time, AR smart glasses have the potential to provide a wider range of information than other fitness trackers, especially visually rich data like maps and navigation or training examples. In addition, embedded cameras on smart glasses can allow users to record activities for later study, so long as a first-person capture perspective is helpful.
The majority of consumer AR smart glasses will be paired with smartphones; consequently, they will provide immediate access to notifications/utility apps, similarly to smartwatches but without needing to check a smartphone or wrist. The introduction of spatial tracking capabilities and more natural interaction methods like gesture and voice will play an essential role in driving demand for AR smart glasses as fitness tracking devices. However, AR smart glasses require multiple improvements in terms of technological capabilities, design, weight, and price range in order to compete with and surpass smartwatch shipments. At the same time, apart from device improvements, AR smart glasses manufacturers also need to define competitive marketing strategies and build strategic partnerships in order to educate the market about device capabilities. Finally, AR smart glasses may face sensor placement issues considering their location; heart rate is an important metric and an appropriate sensor has not yet been seen on smart glasses.
All in all, fitness and sports are a promising area for the AR/VR market given the trends in consumer behavior; however, in order to achieve similar levels of success seen with smartwatches, AR/VR HMDs require a combination of technical/design improvements, more affordable prices, and consumer education.